

Version 1.6.1
David Trew
Consulting Ltd
The Chemistry of Multi-
Part 1: Fundamentals of Multi Protonic Equilibrium
It is well known that the acid-
Solubility and rate of dissolution in the gastrointestinal tract
Permeability across biological membranes
Bioavailability
Stability and degradation under different conditions
Access to the site of action
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Equilibrium constants, which can be expressed either as dissociation constants pKa or protonation constants log K, are normally used to characterize, in numerical terms, the acid base chemistry of compounds that have either a single protonatable site, such as acetic acid 1

pKa = [CH3COO-
[CH3COOH]
Or a compound with well-

pKa1 = [H3N+CH2COO-
log K1= [H3N+CH2COOH]
[H3N+CH2COO-
[H2NCH2COO-
where protonation occurs in a sequential step wise fashion. These equilibrium constants are often called the macroscopic constants. In addition, it is possible to assign a particular equilibrium with protonation of a specific site on the molecule.
However, in a compound with overlapping constants (where ΔpKa < 3), such as urocanic acid (pKa = 3.5, 5.8 and 13) 3, which consists of an imidazole ring and a propenoic acid side chain. The constants K1 and K2, respectively, represented by equation (iii) characterise the acid-
 …..(iii)
…..(iii)
K1 = [UrH] K2 = [UrH2+]
Instead of the sequential stepwise protonation seen with glycine; between pH 1 and 9 urocanic acid establishes the multi-
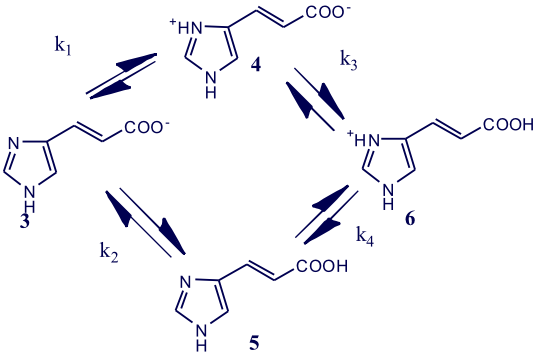
Scheme 1
k1 = [5] k2 = [3] k3 = [6] k4 = [6]
Above pH 9 (but below pH 10) urocanic acid predominantly exists in the urocanate anion represented by structure 4. As the pH of the solution is lowered protonation can occur either at the imidazole nitrogen site to yield the zwitterion represented by structure 5 followed by protonation at the carboxylate site to give the urocanoium cation 6. Alternatively protonation can initially occur at the carboxylate site to yield the neutral urocanic acid molecule, structure 3; this is then followed by protonation at the imidazole nitrogen to give the urocanoium cation 6.
The structures 3 to 6 are called micro-
This should be considered when discussing the acid-
2
pKa2 = [H2NCH2COO-
[H3N+CH2COO-
[H3N+CH2COOH]
[Ur-
[4][H+] [4][H+] [5][H+] [3][H+]